
Options trading is a very popular trading segment in the Indian stock markets yet it is not as easy. There are multiple nuances to options trading and concepts to be considered like options greeks, options trading strategies, effective risk management and strategies to implement on the options expiration day to avoid losses or pitfalls. Here is a brief explanation of the options expiration concept and the strategies that can help to avoid the traps on the options expiration day for European options (CE/PE).

Options expiration refers to the specific date when an options contract becomes void and can no longer be exercised. In simpler terms, it is the last day on which the holder of the option can choose to buy (in the case of a call option) or sell (in the case of a put option) the underlying asset at the agreed-upon price. After this date, the option contract expires and becomes worthless. Options expiration typically happens on the last Thursday of every month for options traded on stock exchanges. This is a crucial day for traders because they must decide whether to exercise their options, sell them, or let them expire.
The importance of options expiration lies in its impact on the market and trading strategies. As the expiration date approaches, the value of options can change rapidly, influenced by factors like the underlying asset's price, time remaining until expiration, and market volatility. Traders need to pay close attention to these changes to make informed decisions and manage their positions effectively. Additionally, options expiration can lead to increased market activity and volatility as traders close out or adjust their positions, which can affect stock prices and overall market movements. Therefore, understanding and planning for options expiration is essential for successful trading.

Some of the common strategies applied at the time of options expiration are explained in brief here.
Rolling Over is a strategy where traders extend their positions to a later expiration date. Instead of letting their current options expire, they sell them and buy new options with a later expiration. This allows traders to stay in the market and potentially profit from future price movements. For example, if a trader holds an option expiring in July but believes the market will move favourably by August, they might roll over their position to an August expiration.
Exercising the Option means the trader decides to use their right to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset at the agreed-upon price before the option expires. This strategy is typically used when the option is "in the money," meaning the current market price is favourable compared to the option's strike price. For instance, if a trader has a call option to buy a stock at Rs. 100, and the stock is trading at Rs. 120, exercising the option can be profitable.
Closing the Position involves selling the option back to the market before it expires. This is a common strategy when traders want to lock in profits or minimise losses without exercising the option. By selling the option, traders can realise its current market value. For example, if an option's value has increased since it was purchased, a trader might sell it to capture the gain.
Letting the Option Expire is a passive strategy where traders do nothing, allowing the option to expire worthless. This approach is typically used when the option is "out of the money," meaning the market price is not favourable compared to the option's strike price. For instance, if a trader holds a call option with a strike price of Rs. 150, but the stock is trading at Rs. 130, they might let the option expire to avoid further losses.
Hedging involves using options to protect against potential losses in an existing position. Traders might buy put options to guard against a decline in the value of stocks they own or buy call options to cover short positions. This strategy helps manage risk by providing a safety net if the market moves unfavourably. For example, if a trader owns shares of a company and fears the stock might drop, they could buy a put option to mitigate potential losses.

Options expiry, as mentioned above, is when the option is no longer viable. Traders have the choice to exercise the option before expiry or to implement strategies that can yield them profits or minimise losses as the case may be. However, this can be tricky. There are some common mistakes that traders need to avoid on the options expiration day to have a sound portfolio. Here is a comprehensive explanation of the same.
Ignoring Time Decay can be a costly mistake on options expiration day. Time Decay refers to the reduction in the value of an options contract as it approaches its expiration date. This happens because the likelihood of significant price movement decreases as the expiration date nears. Traders should be aware that options lose value rapidly in the final days and hours. Failing to account for this can lead to unexpected losses. For example, if a trader holds an option that is out of the money and expects a last-minute market move, the option might still expire worthless due to insufficient time for the price to change favourably.
Overlooking Market Volatility around expiration can be a significant oversight. Options expiration often brings increased volatility as traders adjust or close their positions. This heightened market activity can lead to rapid price swings and unpredictable movements. Traders should be prepared for this volatility and avoid making hasty decisions based on short-term price fluctuations. For example, selling an option in a panic during a volatile period can result in selling at a lower price than intended.
Ignoring Assignment Risk can result in unexpected financial obligations. If traders hold options that are in the money, there is a risk of assignment, which means they may be required to fulfil the contract terms, such as buying or selling the underlying asset. For example, if you hold an in-the-money put option, you might be obligated to sell the stock at the strike price. This can lead to significant capital requirements if one is not prepared. Traders should therefore always be aware of the potential for assignment and manage their positions accordingly.
Ignoring Options Greeks can lead to a lack of understanding of the factors affecting the options' value. The Greeks—Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega, and Rho—measure different risks and sensitivities in an options position. For instance, Theta measures time decay, while Delta measures the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying asset's price. By ignoring these Greeks, traders might miss out on crucial insights into how their options will behave as expiration approaches. Understanding these metrics can help traders make more informed decisions and better manage their risk. For example, a high Theta value might indicate that the option is losing value quickly due to time decay, prompting traders to close or adjust the position.
Failing to Close Out Positions can lead to unwanted exercise and financial obligations. If a trader does not close or roll over positions before expiration, they might be required to buy or sell the underlying asset. This can result in significant costs or capital requirements. For instance, if you have a call option on a stock and do not close it, you might have to purchase the stock at the strike price, which could tie up a large amount of capital. Therefore, traders should always review and manage their positions to avoid unexpected outcomes.
Misjudging Liquidity can affect the ability to execute trades efficiently on the expiration day. As the expiration date approaches, the liquidity of certain options can decrease, making it harder to buy or sell at favourable prices. Low liquidity can lead to wider bid-ask spreads, increasing trading costs. It's crucial to trade options with high liquidity, especially close to expiration, to ensure traders can enter or exit positions without significant slippage.
Not Having a Clear Plan can lead to poor decision-making and potential losses. It is essential to have a well-defined strategy for managing the options positions as expiration approaches. This includes deciding whether to close, roll over, or exercise options based on market conditions and individual trading goals. Without a clear plan, traders might make impulsive decisions that can negatively impact the trading outcomes. For instance, if traders do not have a plan and the market moves against them, they might panic and make a hasty decision, resulting in unnecessary losses.
Read More: Binary Option Trading
Options expiration is a critical time for traders, marked by the final opportunity to exercise or close out options contracts. Understanding the implications of options expiration is essential, as it affects the value of the options and can lead to increased market volatility. Traders must avoid common mistakes, stay informed or vigilant of the complexities of navigating the options expiration effectively and make strategic decisions that align with their trading goals and market conditions.
This blog talks about the meaning of options expiration and the pitfalls to be avoided to have a profitable portfolio. So what do you think of these mistakes and do you have some more to add to the list based on your experience? Let us know and we will discuss them further or address any queries that you may have.
Till then Happy Reading!
Read More: Authorized Realtime Data Hub for NSE, BSE, and MCX
India is increasingly becoming a dominant options trading market with the highes...

A famous quote by legendary investor Mr. Warren Buffet: 'Someone's sitting in th...
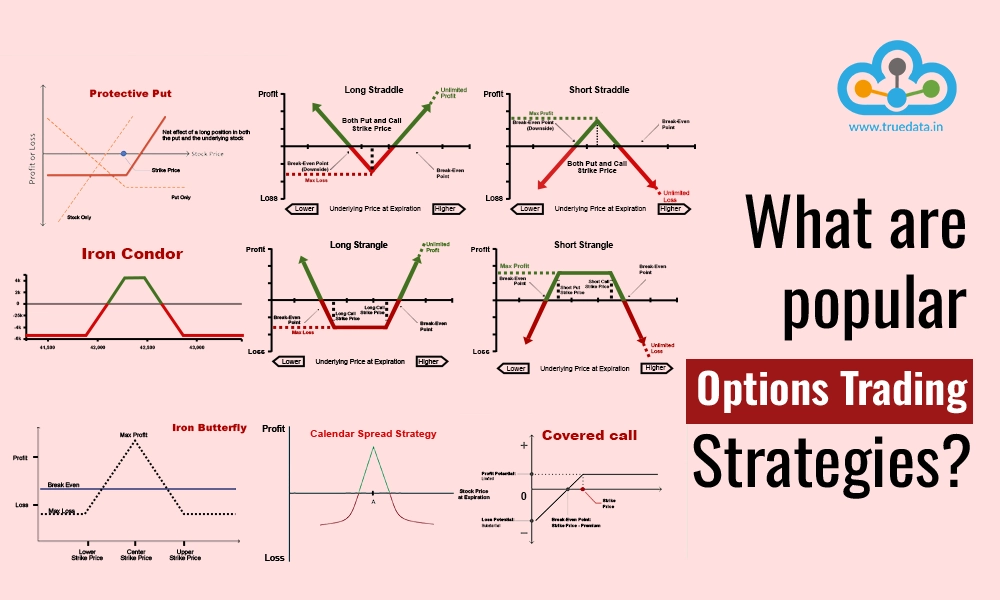
When we talk about trading, which security is the most common one that comes to ...