 The start of the year has not brought good news for stock markets around the globe. There has been severe volatility and growing concerns about recession from many economists and analysts across countries. Despite this, we are seeing many companies planning their IPOs and getting their checklist sorted to be listed on stock exchanges. This calls for the obvious question which is why companies want to get listed. Given here is the answer to this question and other related details. Read More: T+1 Settlement Cycle - All you need to know
The start of the year has not brought good news for stock markets around the globe. There has been severe volatility and growing concerns about recession from many economists and analysts across countries. Despite this, we are seeing many companies planning their IPOs and getting their checklist sorted to be listed on stock exchanges. This calls for the obvious question which is why companies want to get listed. Given here is the answer to this question and other related details. Read More: T+1 Settlement Cycle - All you need to know
The listing of shares in India refers to the process where a company makes its shares available for public trading on a recognized stock exchange in the country. A company going public can raise capital by issuing its shares which are then listed on the country’s stock exchanges NSE and BSE or both. The shares are then traded and the price of the shares is determined based on the demand and supply functions of the market.
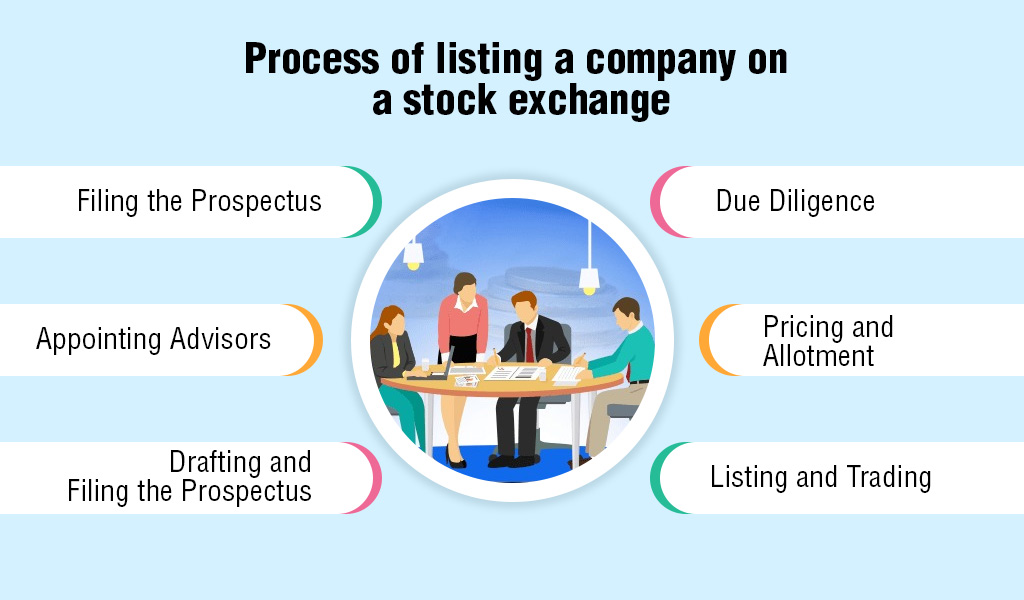 Listing a company on a stock exchange in India involves several steps and compliance with various regulatory requirements. The process can be broadly divided into the following stages.
Listing a company on a stock exchange in India involves several steps and compliance with various regulatory requirements. The process can be broadly divided into the following stages.
The first step towards listing is to ensure that the company meets the eligibility criteria set by the stock exchange and regulatory bodies and legislature like SEBI and Companies Act 2013. The eligibility criteria include several factors like the minimum net worth, profitability, track record, etc.
After ascertaining their eligibility, the applicant company is required to appoint various participants of the IPO namely, merchant bankers, lawyers, auditors, and underwriters who play key roles to assist with the listing process.
The company will need to prepare a prospectus, which is a legal document that provides details about the company, its operations, financials, and the securities being offered. The prospectus must be filed with SEBI and the stock exchange as per the due process.
The stock exchange and SEBI are then required to conduct due diligence on the company and its promoters. This exercise is necessary to ensure compliance with regulations and verify the accuracy of the information provided in the prospectus. They are also entitled to provide comments on these documents and direct changes in the DRHP. Following these changes, the company will then file RHP with SEBI before the launch of the IPO.
The company along with the underwriters will need to determine the price at which the securities will be offered to investors as well as the number of securities to be allotted. Most IPOs are book-built IPOs in India and the price band determined by these participants is mentioned in the RHP for different categories of investors to subscribe.
Once the securities are allotted to eligible investors, the company's shares will be listed on the stock exchange, and they can be traded based on the market price of the security.
The listing of a company on the stock exchange is filled with both pros and cons. Given here is a brief list of the same.
 Some of the prime benefits of listing a company on the stock exchange are given hereunder.
Some of the prime benefits of listing a company on the stock exchange are given hereunder.
The primary benefit of listing a company is getting access to public money. This helps them efficiently raise funds by selling their shares to the public. These funds can be used for strategic purposes like the acquisition of a new plant or machinery for the business, expansion of the business, diversification of business or acquiring new subsidiaries, meeting working capital needs, or paying off debts.
A listed company is subject to many stringent rules and regulations relating to the transparency, accuracy, and reporting of financial statements to safeguard the public interest. These enhanced regulations provide more credibility and trustworthiness to the listed company further increasing the confidence of the investors and increasing the ability of the company to raise more funds.
Listing a company on the stock exchange also allows for higher liquidity of company shares. These shares can be bought and sold freely by investors which is also instrumental in attracting more investors to the company and enhancing its marketability.
Listed companies can get access to many regulatory benefits, such as tax exemptions, access to international investments, and access to government schemes and initiatives. These benefits provide additional incentives for companies to list on stock exchanges for easier access to credit.
Companies usually offer stock options and other equity-based incentives to employees, which can help to attract and retain top talent. A listed company will benefit such employees too as they can get better returns on their stock options and enhanced liquidity.
 Although there are multiple benefits for a company to be listed on a recognised stock exchange, there are a few downsides to it too. These limitations are mentioned hereunder.
Although there are multiple benefits for a company to be listed on a recognised stock exchange, there are a few downsides to it too. These limitations are mentioned hereunder.
One of the many limitations of listing a company on stock exchanges is the high cost of the process. These costs include high legal and accounting fees, underwriting fees, and ongoing regulatory compliance costs. Such costs are often a deterrent for companies from listing on stock exchanges, especially in the case of small entities with limited access to funds.
According to SEBI, Companies Act, 2013, and other related legislations in India, listed companies are required to make regular disclosures of financial and other information from time to time. This can be a quite cumbersome, time-consuming, and costly affair for some companies.
Companies that are listed on the stock exchange are subject to more regulations and compliance requirements, which can be time-consuming and costly.
When a company goes public, it entails the sharing of control with a larger group of shareholders. This can limit the control that the founders, promoters, and management team have over the company's direction.
Listing a company on stock exchanges is a detailed process that involves months of careful planning and execution. Companies need to primarily meet all the eligibility requirements to be listed on stock exchanges and ensure proper compliance with all the rules and regulations in this regard. Although market volatility is a part and parcel of being listed on the stock exchange, the multiple benefits of listing outweigh such risk of volatility. It is one of the many reasons why despite growing concerns like recession and inflation, many companies are still in the process of being listed on stock exchanges. Hope this article was informative enough to make you understand why companies, especially start-ups, prefer being listed on stock exchanges. Do let us know if you have any questions related to the listing of companies or any other related concepts. Till then Happy Reading!

Introduction In an attempt to curb speculative trading, the exchanges move stoc...
Introduction Real Time Data from NSE, BSE & MCX is distributed to various d...

Indian Stock market has two leading stock exchanges - BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange...