
Mutual funds are the go-to investment option for different categories of investors whether they are new or seasoned players in the investment arena. However, did you know mutual funds are categorised into multiple types based on various parameters? Here is a detailed insight into the various types of mutual funds available for investment.
This is the primary categorisation of mutual funds and refers to how the mutual fund is organised and managed. The main types include,
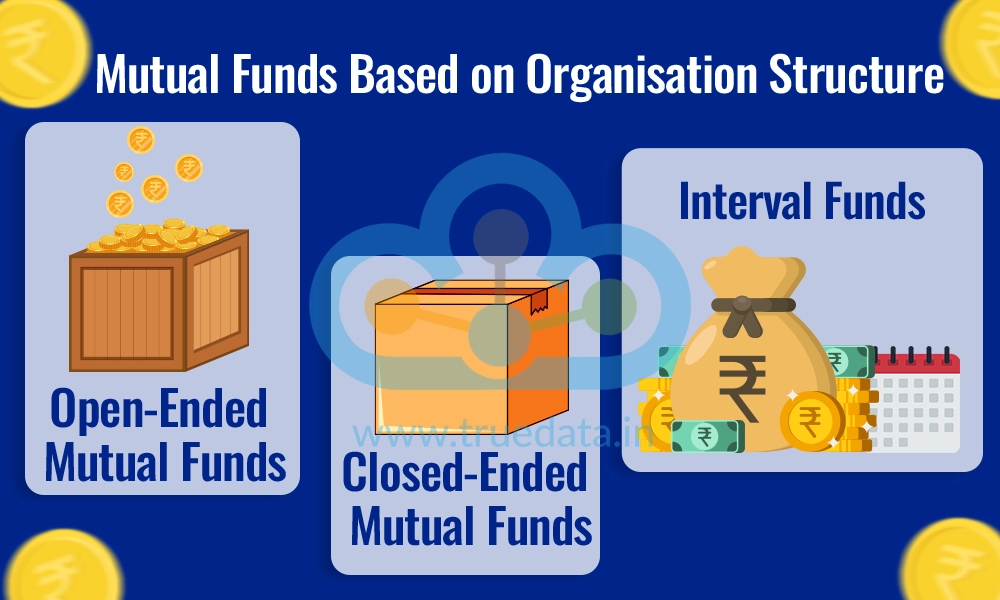
Open-ended mutual funds are the most common type of mutual fund in India. These funds allow investors to buy and sell units at any time directly from the fund. There is no fixed maturity period, which means that investors can enter or exit the fund at their convenience. The Net Asset Value (NAV) of the fund is calculated daily, and transactions occur at this value. Open-ended funds offer liquidity, making them highly flexible for investors who may want to adjust their investments according to market conditions or personal needs.
Advantages -
Easy entry and exit.
Suitable for long-term as well as short-term investors.
Offers high liquidity as investors can redeem their units anytime.
Closed-ended mutual funds have a fixed maturity period, unlike open-ended funds. In these funds, investors can subscribe only during the initial launch period (New Fund Offer or NFO), and after that, no new investors can join. Once the investment period starts, the fund is listed on the stock exchanges and investors can only buy or sell units through the stock market at the prevailing price, which may differ from the NAV.
Advantages -
Suitable for investors who can lock in their money for a specific period.
Fund managers have more control over the portfolio since they do not have to manage frequent cash inflows and outflows.
Interval funds are a hybrid between open-ended and closed-ended funds. These funds allow investors to buy or sell units only during specific periods known as ‘intervals’ (which may occur every six months, annually, or quarterly) which makes them similar to open-ended funds. Outside of these intervals, no transactions are allowed which makes them similar to close-ended funds during these durations. These funds may invest in equity, debt, or a mix of both.
Advantages -
Suitable for investors looking for a structured investment with limited liquidity.
Offers more flexibility than closed-ended funds, as there are periodic windows to enter or exit the fund.

The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) and the Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI) recognise different types of funds based on whether the portfolio is managed actively or passively. Understanding this distinction is important for investors to know how their money is handled and what returns to expect. The main types include,
In an actively managed mutual fund, the fund manager plays a key role in actively selecting and managing the portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. The goal of the fund manager is to beat the market or outperform a specific benchmark index by making informed decisions on which assets to buy, hold, or sell. The fund manager conducts extensive research, analyses market trends, studies company performance, and adjusts the portfolio based on their judgement.
Advantages -
Potential for higher returns if the fund manager’s decisions are successful.
Can adapt to changing market conditions, offering the opportunity to capitalise on market trends.
Risks -
Higher management fees due to the active involvement of the fund manager.
There is no guarantee of beating the market as fund performance depends heavily on the skill of the fund manager.
Passively managed mutual funds aim to mirror the performance of specific benchmark indexes such as the Nifty 50 or Sensex. In these funds, the fund manager does not actively select stocks but simply builds a portfolio that replicates the components of the chosen index. The goal is to match the index's performance, not beat it. This style of management requires less involvement and decision-making by the fund manager.
Advantages -
Lower management fees compared to actively managed funds since there is no need for in-depth research or active trading.
These funds tend to be more transparent because the holdings reflect the index they track.
Suitable for investors looking for stable, predictable returns over time.
Risks -
Limited potential to outperform the market, as the returns depend solely on the performance of the underlying index.
If the market or index performs poorly, the fund will too, as it cannot adjust to avoid downturns.
Mutual funds are also categorised based on their investment objectives, which define the primary goal the fund seeks to achieve. The different types of funds based on investment objectives include,

Equity mutual funds primarily invest in stocks or shares of companies and are designed to generate capital appreciation over time. The main objective of equity funds is long-term wealth creation, making them suitable for investors who are willing to take on higher risk for potentially higher returns. These funds aim for growth by investing in companies with the potential to increase in value over time.
Equity funds are further classified into different categories by SEBI based on factors like market capitalisation, investment strategy, tax-saving options and more. These categories are explained below,
.webp)
Debt funds invest in fixed-income securities like government bonds, corporate bonds, treasury bills, and other debt instruments. The primary objective of debt funds is to provide regular income with lower risk compared to equity funds. They are ideal for conservative investors who prioritise capital preservation over high returns.
Debt mutual funds are further classified into many categories by SEBI based on the debt instruments they invest in. The types of debt funds include,
.webp)
Hybrid funds invest in a mix of equity and debt instruments, aiming to strike a balance between growth and income. The objective is to provide a combination of capital appreciation and regular income, with a moderate level of risk. By investing in both asset classes, hybrid funds offer diversified exposure and can cushion the impact of market volatility.
The SEBIincludes classification of hybrid funds ,.webp)
Solution-oriented funds are designed with specific financial goals, such as retirement planning, savings or children’s education. These funds come with a recommended lock-in period, encouraging investors to stay invested for the long term to achieve their financial goals. This fund category is explained hereunder.

Retirement funds are mutual funds focused on helping investors save for retirement through long-term capital growth. They come with a lock-in period or stay invested until the investor turns 60, ensuring dedication to retirement goals. These funds usually start with a higher allocation to equities for growth, gradually shifting to debt to reduce risk as retirement nears. Retirement funds may also provide tax benefits under Section 80C, making them ideal for individuals aiming to build a stable retirement corpus over time.
Children’s funds are mutual funds designed to help parents save for future expenses like education or marriage. They come with a lock-in period or are accessible once the child reaches a certain age, encouraging long-term investment. These funds balance growth and stability by investing in both equity and debt, depending on the fund’s objective and investment horizon. Children’s funds are suitable for parents planning for major milestones, ensuring financial security without depleting other savings like retirement funds.
The mutual funds that do not fall under any of the above categories specifically are classified under the other schemes as per SEBI and AMFI. These funds include,

Index Funds are mutual funds designed to mirror the performance of a specific stock market index, like the Nifty 50 or Sensex. By investing in the same stocks and in the same proportions as the index, they offer market returns at a low cost, as they do not require active management. Index funds are ideal for investors seeking a low-cost, hands-off way to participate in the overall market or specific sectors without the need for stock picking.
ETFs are funds traded on stock exchanges, similar to individual stocks, and can track indices, commodities, or bonds. They offer diversification, liquidity, and the flexibility to be bought or sold at any time during market hours. With generally low expense ratios, ETFs are suited for investors seeking cost-effective, transparent, and flexible access to various markets or sectors.
Gold ETFs invest in physical gold or related assets, providing investors with an easy and cost-effective way to gain exposure to gold without the need for storage. Each unit of a Gold ETF corresponds to a specific amount of gold, and its value aligns with gold prices. Ideal for hedging against inflation or economic uncertainties, Gold ETFs provide liquidity and ease of trading.
International funds, or global funds, invest in assets outside India, giving investors exposure to foreign markets. These funds help diversify portfolios by spreading investments across different economies, reducing reliance on the Indian market. Suitable for investors aiming for geographical diversification, these funds carry additional risks, including currency fluctuations and global market volatility.
A Fund of Funds (FoF) invests in other mutual funds rather than directly in securities, providing broad diversification across asset classes and fund types in a single investment. Managed by professionals, FoFs simplify portfolio building for investors. Though convenient, they may come with slightly higher fees due to the costs of managing both the FoF and the underlying funds.
Mutual funds are often considered to be a perfect investment vehicle as they cater to almost every class of investors and also offer multiple benefits. These different classes of mutual funds come with their own set of pros and cons allowing investors to choose a fund that best aligns with their individual investment parameters.
This is a detailed insight into the types of mutual funds available in India. Let us know if you want to know more on this topic and we will be taking up each of these funds separately in our coming blogs to give you further details on each of them.
Till then Happy Reading!
Read More: Concentrated Stock Baskets or Mutual Funds - Which way to go?
Introduction For the longest time, investment in stock markets was thought to b...

One of the primary points of comparison while picking between two or more invest...

Introduction For the longest time, investment in stock markets was thought to b...