
The stock market is a dynamic arena, often marked by sharp swings that demand traders stay vigilant and adaptable. Monitoring market movements is crucial, but understanding the real-time value of assets is even more vital for making strategic decisions. This is where the mark-to-market (MTM) concept comes into play. MTM helps traders and investors pinpoint the current value of their investments, allowing them to identify strategic entry and exit points. Dive into the world of mark-to-market and discover its extensive applications across various financial domains.
Mark-to-market (MTM) is a financial accounting method that values assets and liabilities at their current market prices rather than their historical costs. This means that the value of their investments is updated regularly to reflect the prevailing market conditions. If the market price of an asset increases, its value in the portfolio also increases, and if the market price decreases, the value in the portfolio decreases accordingly. This approach provides a more accurate and transparent picture of a portfolio's value, enabling more informed decision-making based on the most recent data. MTM is particularly beneficial in volatile markets, where prices can experience significant fluctuations, as it helps assess the true value of investments, identify profitable opportunities, and manage risks more effectively.
Mark-to-market (MTM) is a method of valuing assets and liabilities based on their current market prices, rather than their purchase prices. At the end of each trading day, the value of an asset is adjusted to its current market price. Here's a detailed explanation of how it works along with an example.
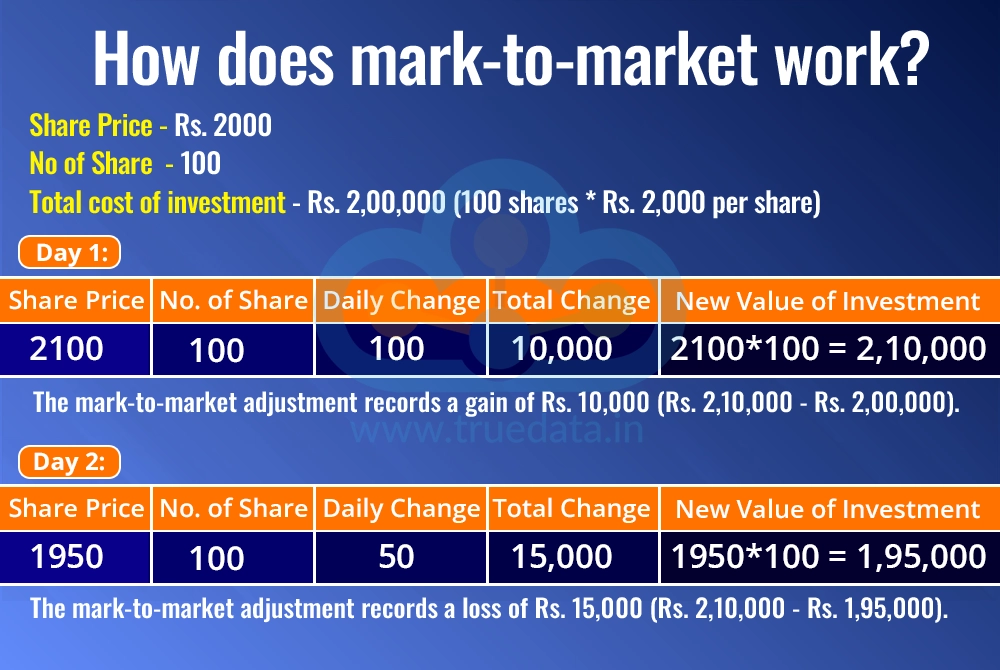
Consider an investor who bought 100 shares of Reliance Industries at Rs. 2,000 per share. The total cost of investment is Rs. 2,00,000 (100 shares * Rs. 2,000 per share).
Day 1
At the end of the trading day, the market price of Reliance Industries shares rises to Rs. 2,100.
The new value of the investment is Rs. 2,10,000 (100 shares * Rs. 2,100 per share).
The mark-to-market adjustment records a gain of Rs. 10,000 (Rs. 2,10,000 - Rs. 2,00,000).
Day 2
The next day, the market price fell to Rs. 1,950.
The new value of the investment is Rs. 1,95,000 (100 shares * Rs. 1,950 per share).
The mark-to-market adjustment records a loss of Rs. 15,000 (Rs. 2,10,000 - Rs. 1,95,000).
Mark-to-market (MTM) is a vital accounting practice for traders and investors as it reflects the real-time value of their assets and liabilities. The importance of mark-to-mark for investors is explained below.
MTM ensures that the financial statements of traders and investors accurately reflect the current market value of their holdings. Instead of relying on historical cost, which may not represent the asset's true worth, MTM updates the value daily. This provides a more realistic and up-to-date picture of one’s financial position.
MTM provides more transparency into the financial health of a portfolio for traders. They can see the true value of their assets and liabilities, making it easier to assess their investment performance. This transparency helps in making informed decisions about buying, holding, or selling assets based on their current market value.
MTM helps traders and investors manage risk more effectively. By regularly updating the value of assets, it becomes easier to identify and respond to market changes. For instance, if the value of a security drops significantly, an investor can take timely action to mitigate losses, such as selling the asset or adjusting their portfolio.
MTM is also essential for compliance with regulatory requirements. Market regulators, such as the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), mandate the use of MTM to ensure that financial statements are accurate and transparent. This helps maintain the integrity of financial markets and protects investors.
MTM is crucial for traders, especially those dealing with futures and options. Brokers use MTM to assess whether a trader’s account has enough funds to cover potential losses. If the market moves unfavourably, the trader might receive a margin call, requiring them to deposit additional funds to maintain their positions. This helps prevent excessive risk-taking and ensures that traders have sufficient collateral.
The advantages and disadvantages of using the mark-to-market strategy are explained hereunder.
Mark-to-market accounting provides a realistic and up-to-date valuation of assets and liabilities. This means that the financial statements reflect the current market conditions, giving a clearer picture of a company's financial health. For traders and investors, this transparency is crucial for making informed decisions.
With mark-to-market, the performance of investments can be evaluated more frequently, typically on a daily basis. This allows traders and investors to quickly identify trends and make timely adjustments to their portfolios, which can be particularly beneficial in volatile markets.
Mark-to-market helps in identifying and managing risks by providing a real-time assessment of portfolio values. This allows traders and investors to promptly address potential issues, such as declining asset values, thereby minimising losses.

The prime shortcomings of using the mark-to-market strategy are,
Mark-to-market can introduce significant volatility into financial statements, as asset values are adjusted to reflect current market conditions. This can lead to fluctuating earnings reports, which may be unsettling for investors and can affect a company's stock price.
Since mark-to-market records the current market value, it includes unrealised gains and losses. These are paper profits or losses that have not yet been realised through actual transactions. This can give a misleading impression of an investor's or company's financial position.
Implementing mark-to-market accounting can be complex and costly. It requires sophisticated valuation techniques and regular updates, which can be resource-intensive. The costs and effort involved might outweigh the benefits, especially in the case of smaller investors or firms.
Mark-to-market (MTM) is a valuable strategy for traders and investors in India as it provides a clear and accurate picture of the current value of their assets. While it offers real-time insights and enhances risk management, it also brings challenges like increased volatility and potential short-term focus. Therefore it is important to have a comprehensive understanding of this strategy for its effective implementation.
Mark-to-market is one of the fundamental concepts of futures and options trading we have addressed it in this blog in a simplified manner. Let us know if you need further details on this topic or have any queries and we will address them.
Till then Happy Reading!
Read More: What is Margin Trading and how is it useful?

Thestock markets are always in a constant dance of ebb and surge of the market s...

Stock trading is not a simple and straightforward concept and requires a detail...
The use of technical analysis for trading is vital for creating a successful tr...