
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) alludes to the method involved with offering portions of a private enterprise to general society in another stock issuance. An IPO permits an organization to raise capital from public financial investors. The change from a private to a public organization can be a significant time for private financial investors to completely acknowledge gains from their venture as it normally incorporates an offer premium for current private financial investors. In the interim, it likewise permits public financial investors to partake in the contribution. In the year 2017, India saw upwards of 36 Initial Public Offerings (IPOs). Accordingly, organizations raised a record Rs. 67,147 crores in the value market through IPOs.
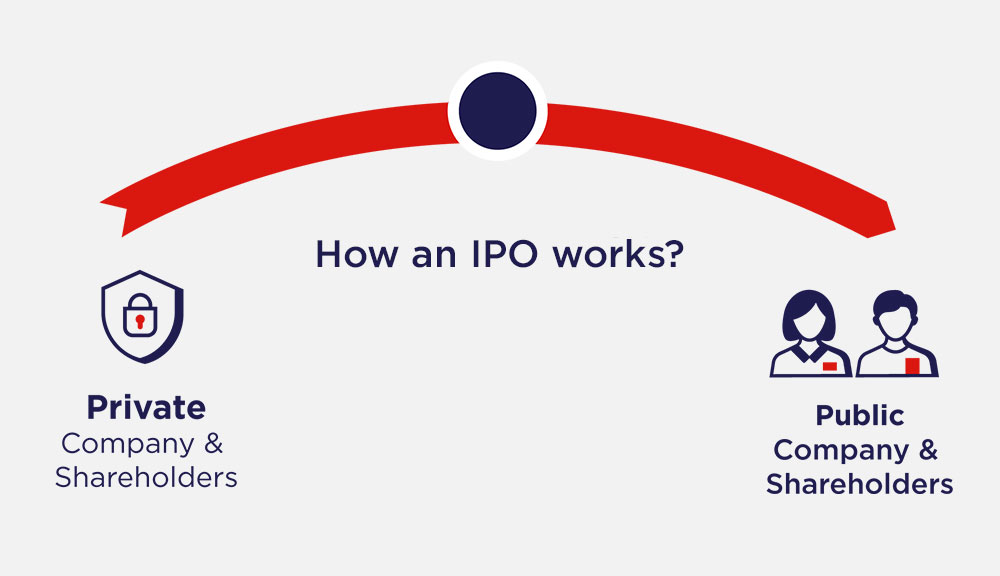 Shares of an organization are presented to the overall population, like an IPO. The Company will raise capital and it will be recorded in the stock trade. To finish the most common way of changing over a privately owned business into a fruitful public organization, it will require a group of outside master guides like examiners, legal advisors, financiers, and bookkeepers to manage the special difficulties which come to their direction.
Shares of an organization are presented to the overall population, like an IPO. The Company will raise capital and it will be recorded in the stock trade. To finish the most common way of changing over a privately owned business into a fruitful public organization, it will require a group of outside master guides like examiners, legal advisors, financiers, and bookkeepers to manage the special difficulties which come to their direction.

Among the issues SEBI addresses through this new system is that self-confirmed organization banks (SCSBs) should distinguish a nodal offer for IPO applications that are handled through UPI as an installment component. The subtleties of the handling would be submitted to SEBI within seven working days. As a component of the new system, SEBI orders that dealers and venture financiers should repay any IPO candidates for oversights by paying Rs multi-day or 15% interest per annum on the application sum, contingent upon which one of the two is higher. Likewise, to guarantee simplicity of working together, the support banks will have an entrance for go-betweens beginning from the date of the IPO till the date it is recorded. This entry will contain all subtleties of any order obstructs or unblocks, the exhibition of UPI handles, applications, and any personal time or deferrals across mediators. Any cycle that affects the offering system of the IPO will be reported. The middle people in an IPO incorporate dealer investors, guarantors, brokers, and enlistment centers and are enrolled by SEBI. These middle people play out all IPO-related exercises including the planning of draft offer reports, the premise of portion, and attributing of offers to the fruitful candidates of IPOs. Further, organizations moving from the IGP to the mainboard will be permitted to do as such under permissive qualification standards. If the organization doesn't fill benefits, total assets, and net resources necessities, the underlying rules that such organizations require 75% of its capital held by Qualified Institutional Buyers (QIBs) has been diminished to half.
 This stage during the time spent IPO comes ordinarily toward the finish. The guaranteeing organization fixes the band, and the offering system is either helped out through a speculation bank or gathering organizations who have some expertise in protections. The ideal offer cost simply keeps the interest marginally higher than the stockpile. This will bring about a respectably steady and consistent increment in secondary selling cost. There are two techniques for fixing the IPO cost. Fixed value technique – The guarantor and friends cooperate to fix a cost for their portions. They account for the liabilities, the objective funding to be accomplished, and the requests of stocks and every connected detail to think of a cost. Book building technique – Here the financier and the organization will fix a value band inside which the financial backers can offer. The last cost is subject to the interest of the offers, the biddings got and the objective cash-flow to be accomplished. Except for framework organizations and banks, most organizations are allowed to set their portion value band. The Company is permitted to set the cap cost at 20% higher than the floor cost.
This stage during the time spent IPO comes ordinarily toward the finish. The guaranteeing organization fixes the band, and the offering system is either helped out through a speculation bank or gathering organizations who have some expertise in protections. The ideal offer cost simply keeps the interest marginally higher than the stockpile. This will bring about a respectably steady and consistent increment in secondary selling cost. There are two techniques for fixing the IPO cost. Fixed value technique – The guarantor and friends cooperate to fix a cost for their portions. They account for the liabilities, the objective funding to be accomplished, and the requests of stocks and every connected detail to think of a cost. Book building technique – Here the financier and the organization will fix a value band inside which the financial backers can offer. The last cost is subject to the interest of the offers, the biddings got and the objective cash-flow to be accomplished. Except for framework organizations and banks, most organizations are allowed to set their portion value band. The Company is permitted to set the cap cost at 20% higher than the floor cost.

An IPO is a firmly watched market. It very well might be a tremendous open door or may end up being a misfortune-making venture. A few IPOs might be excessively advertised by speculation banks which can prompt introductory misfortunes. Nonetheless, most of IPOs are known for acquiring in transient exchanging. Initial public offerings are known for having the unpredictable first day of the season returns, which can draw in financial backers hoping to profit from the limits. Over the long haul, an IPO's cost, as a rule, sinks into a consistent worth.

The year 2021 and 2022 have brought a string of IPOs from companies belonging ...

The year 2024 despite its despite its various ups and downs was a great year for...

On July 3rd, 2023, Sensex created history by reaching the 65000 mark; barely 16...